Get to Grips with Sun Allergy: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Sun allergy is a skin reaction to exposure to sunlight, often presenting as small, itchy spots that can spread and become quite uncomfortable. Symptoms of sun allergy include red rashes and itching.
It's crucial to take preventative measures against sun allergy, such as using sunscreen, seeking shade when the UV index is over 3, and avoiding the sun from noon to 3 PM.
Table of contents
What is a Sun Allergy?
A sun allergy occurs when the skin reacts to the sun's UV rays, causing symptoms like itching, rash, and swelling of the skin.
Definition and Symptoms
Sun allergy is characterized as a skin condition that arises after exposure to sunlight. This condition causes the skin to abnormally react to the ultraviolet light from the sun. People with this condition often experience symptoms like red rashes, itching, and burning on parts of the body exposed to sunlight.
These reactions can occur a few minutes to hours after sun exposure.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or eczema-like rashes that typically cover small or large areas of the skin. In some cases, the symptoms can become more pronounced and lead to blisters or small bumps, causing discomfort or pain.
Areas of the skin usually covered by clothing are rarely affected. This reaction occurs as part of the skin's defense mechanism against the damage caused by UV rays.
Sun rash
Sun rash typically appears as red and itchy rashes on the skin after sun exposure. It can be prevented by wearing a sun hat, using high SPF sunscreen, and avoiding overexposure between noon and 3 PM.
Types of Sun Allergy
Sun allergy manifests in various ways, depending on the type. This makes it important to know the different types to better manage the condition.
1. Benign sun allergies: Most often affects young women between the ages of 25 and 35. Typical symptoms include itchy red bumps that appear on parts of the skin exposed to sunlight, such as the neckline, underarms, and face. It is one of the most common forms of light sensitivity.
2. Photoallergic reaction: Occurs when the skin reacts to a combination of sunlight and certain chemicals or substances the person has been exposed to. These can be perfumes or even sunscreens. The symptoms resemble those of eczema with redness, peeling, and itching.
3. Solar urticaria: This rare form of sun allergy causes hives on the areas of the skin that have been exposed to sunlight. Urticaria can occur within minutes of exposure to UV rays and can cause intense itching and redness.
Each type of sun allergy requires its specific treatment and prevention method. Recognizing which type you suffer from is the first step towards better protection against the sun's rays.
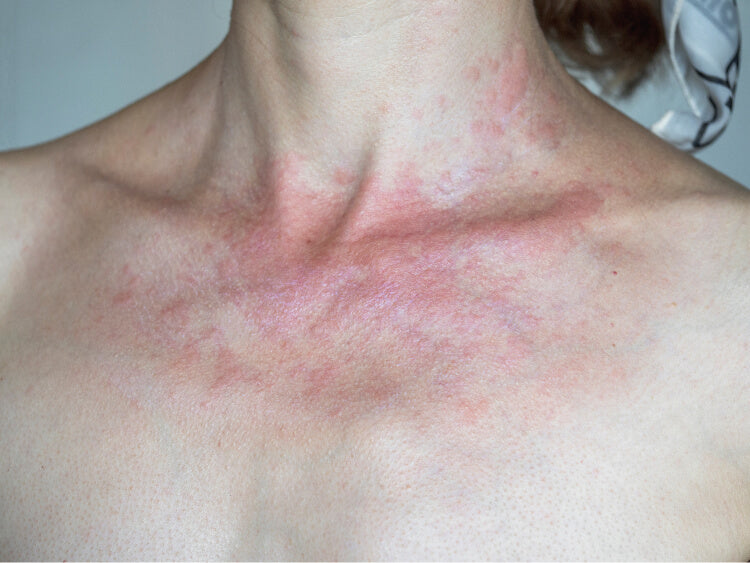
Causes of Sun Allergy
Sun allergy arises due to the body's hypersensitivity to the sun's rays. It may also be related to genetic predisposition and certain risk factors.
Genetic Predisposition
Some people are more prone to develop sun allergy due to their heritage. This is due to genetic factors that make their skin more sensitive to the sun's rays. Various forms of sun allergy, such as polymorphic light eruption and Sun rash, may also have different genetic causes.
If a family member has had a sun allergy, the risk of developing the condition may be higher. Understanding your own genetic risk can help in taking precautions against sun allergy. Preventive steps include using sun protection products and avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun.
This is particularly important for individuals with a family history of allergic reactions to UV light. Genetics play a significant role, but by taking the right steps, you can reduce the risk of developing a sun allergy.
Sensitivity to the Sun's Rays
The sun's rays can cause hypersensitivity, resulting in a sun allergy. Exposure to UVA and UVB rays can trigger hypersensitivity reactions in some individuals, experiencing itching, rash, or other unpleasant reactions on the skin.
Sun allergy can also be due to a genetic predisposition, increasing sensitivity to the harmful effects of the sun. Excessive exposure to the sun combined with a predisposition for hypersensitivity can exacerbate the condition.
It is important to be aware of these reactions and take appropriate precautions to avoid severe symptoms. Sun allergy can present itself as small, itchy dots that spread and can be very uncomfortable, especially in the spring. High SPF sunscreens and UV-protective clothing are useful tools to protect against the harmful effects of the sun.
Risk Factors
According to dermatologists, up to 10-15% of the population may be affected by sun allergy. There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing sun allergy, including:
1. Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with family members who have suffered from sun allergy are at increased risk of developing this condition.
2. Sensitivity to Sun Rays: People with increased sensitivity to UVA and UVB rays from the sun are at a higher risk.
3. Certain Medications: The use of certain medications can increase the risk of developing sun allergy.
4. Frequent Exposure: Prolonged or repeated exposure to the sun's rays without adequate protection can contribute to the development of sun allergy.
It's important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate steps to minimize exposure and protect against the harmful effects of the sun.
Treatment and Prevention of Sun Allergy
Protect your skin by applying and avoiding the sun during the most intense hours of the day. Wear sunglasses and clothes to shield your skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
Feeling uncomfortable? Consult a doctor to find appropriate medication for treating sun allergy.
Focus on Sun Protection
Sun protection is crucial to prevent sun allergy. Protection from the sun’s harmful effects can be achieved by following these practical guidelines:
1. Always use sunscreen with a high protection factor, such as SPF 30 or higher, and make sure to reapply it regularly throughout the day.
2. Wear protective clothing, including hats and sunglasses, to shield the skin from UVA and UVB rays.
3. Seek shade and avoid direct sun exposure during the most intense hours between 12 PM and 3 PM.
4. Consider using umbrellas or other forms of shade during outdoor activities.
Remember, it is vital to take these steps to effectively protect your skin from the damaging effects of the sun.
Avoid Prolonged Sun Exposure
Avoid staying in direct sunlight for long periods to prevent sun allergy. Wear clothing that covers the skin and seek shade, especially during the most intense sun hours. When outdoors, use plenty of high-protection-factor sunscreen and wear a hat or sunglasses to shield yourself from UVA and UVB rays.
Also, remember to stay hydrated and seek shade to avoid overexposure to the sun.
Use of Special Products for Sun Allergy
When it comes to preventing and alleviating the symptoms of sun allergy, the use of special products plays a crucial role. Specially formulated dermocosmetic care products can help reduce itching and improve skin comfort for those suffering from sun allergy.
These products have proven effective in limiting the uncomfortable symptoms, such as redness, itching, and irritation caused by sun allergy. By integrating these special products into one's daily skincare routine, relief can be achieved and the quality of life for those with sun allergy can be improved.
There are also products specially developed to protect the skin from UVA and UVB rays and strengthen the skin barrier to better withstand sun-related reactions. These products contain ingredients that soothe and restore the epidermis after sun exposure, helping to prevent and reduce the extent of sun allergy symptoms.
Medications for Treating Sun Allergy
Antihistamines and steroid creams can be used to alleviate the symptoms of sun allergy. These medications can help reduce itching, rash, and swelling caused by sun allergy.
It's important to consult a doctor to get the correct dosage and application of these medications. Protection from the sun should still be a priority, even when taking medication for sun allergy, as it can help prevent further reactions on the skin.
Ensure to follow the prescribed advice from your doctor and avoid sun exposure during the most intense hours of the day to minimize the risk of sun allergy.
Other Skin Reactions Due to the Sun
Other skin reactions to the sun can cause discomfort and irritation, including polymorphic light eruption. These conditions can be treated with first aid and prevention measures to relieve symptoms and avoid recurrences.
Polymorphic Light Eruption
Polymorphic light eruption presents with various outbreaks that vary in size and appearance. When the skin is exposed to the sun, it can cause itchy rashes, redness, swelling, and blisters.
It's important to seek professional help from a dermatologist to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment of polymorphic light eruption. It is a rarer type of sun allergy, but it is important to be aware of the symptoms and take the necessary precautions to avoid sun exposure.
Polymorphic light eruption can significantly impact one's quality of life, and it's crucial to understand how to best protect against this condition. People with polymorphic light eruption should avoid direct sunlight as much as possible, use sunscreen with a high protection factor, and wear protective clothing and sunglasses.
First Aid for These Conditions
When experiencing skin reactions to the sun, you can alleviate symptoms by following these step-by-step tips:
1. Cooling: Apply cool compresses or wraps to reduce itching and irritation.
2. Soothing Creams: Use soothing creams or lotions with aloe vera to calm inflammation and promote healing.
3. Avoid Rubbing: Refrain from rubbing or scratching the affected areas to prevent further irritation reactions.
4. Hydration: Drink plenty of water to maintain body hydration and strengthen the skin’s natural protective mechanisms.
These simple steps can help relieve discomfort and speed up the healing process after skin reactions from the sun.
Conclusion
Preventing sun allergy is crucial to avoid symptoms like itchy spots and discomfort in the spring. Protect yourself from UV rays by wearing a sun hat, using sunscreen, and avoiding overexposure.
Use sunscreen with nourishing ingredients for the face, and remember to reinforce protection after water activities. It is also important to seek shade and use sun protection, especially when the UV index is high.
By following these steps, you can minimize the risk of sunburn, photosensitivity, and other negative effects of the sun.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of sun allergy?
Symptoms of sun allergy may include redness, itching, and small blisters on the skin, which appear after exposure to sunlight, specifically UVA and UVB rays.
How can sun allergy be treated?
Treating sun allergy can involve using creams that lubricate and soothe the skin, avoiding direct sunlight and tanning beds, and using allergy medications, such as those also used for hay fever.
Are there ways to prevent sun allergy?
To prevent sun allergy, one should limit time in direct sunlight, especially between 12 PM and 3 PM, use high-factor sunscreen, cover the body with clothing, and wear a hat and sunglasses.
Can one get sun allergy from using a sunbed?
Yes, one can develop sun allergy from using a sunbed, as it exposes the skin to intense UVA rays, which can trigger or exacerbate symptoms of sun allergy.



